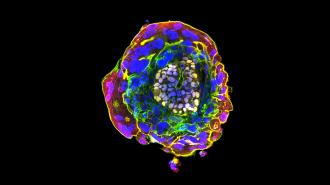
A Cambridge University scientist says her research lab has used stem cells to create a human embryo that developed past day 14. If confirmed, the technique could lead to breakthroughs for treating everything from fertility problems to genetic disorders.
The challenge: We can’t see what’s happening in the womb during the earliest stages of pregnancy, but by studying donated embryos in the lab, scientists have made valuable discoveries into infertility, the causes of miscarriages, and more.
The important developmental period between days 14 and 28 is largely a mystery.
There aren’t enough donor embryos to meet the demand, though, so researchers have started making human embryo models, usually from stem cells, to help close the gap. These aren’t identical to “natural” embryos, though, and they can’t develop indefinitely — a model created at Monash University, for example, could only mimic the first 10 days after fertilization.
As for how long scientists could develop donor embryos in the lab, we don’t actually know — until recently, ethical guidelines have strictly forbidden cultivation past day 14. That has left the important developmental period between days 14 and 28 largely a mystery.
Faux human embryo: Developmental biologist Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz has now announced that her Cambridge-Caltech lab has used stem cells to create human embryo models that survived just past what would be day 14 for a natural embryo, according to a report by the Guardian.
“It’s beautiful and created entirely from embryonic stem cells,” Żernicka-Goetz told the Guardian before announcing the breakthrough during a plenary address at the International Society for Stem Cell Research’s annual meeting in Boston on June 14.
The big picture: Żernicka-Goetz’s team has yet to publish anything on their research, which makes it hard to say just how scientifically significant it may be — we still don’t know exactly how closely the embryo models mimic a natural human embryo, for example.
If the team has found a way to create embryo models that are identical (or close) to a natural human embryo and can develop for up to 14 days, they could potentially supply breakthrough scientific research.
“It is important that research and researchers in this area proceed cautiously, carefully, and transparently.”
James Briscoe
If the embryo models can continue maturing in the lab beyond 14 days, they could give researchers an opportunity to see into that important stage of development — but whether they’d be able to take advantage of that opportunity isn’t yet clear.
“Unlike human embryos arising from [IVF], where there is an established legal framework, there are currently no clear regulations governing stem cell-derived models of human embryos,” said James Briscoe, a senior group leader at the Francis Crick Institute, who wasn’t involved in the research.
According to Briscoe, there is now an “urgent need” for such a framework.
“It is important that research and researchers in this area proceed cautiously, carefully, and transparently,” he continued. “The danger is that missteps or unjustified claims will have a chilling effect on the public and policymakers. This would be a major setback for the field.”
We’d love to hear from you! If you have a comment about this article or if you have a tip for a future Freethink story, please email us at tips@freethink.com.